
The Five Most Common Use Cases Organisations are Tackling with Next Generation Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
Author: Jake Hammacott
Release Date: 13/06/2023
Secure Web Gateways (SWGs) are often used to control and manage access to or from websites within organisations to protect the user from malicious content. Granular policies are set and enforced to act as a security gateway, stopping threats from accessing web based applications.
Netskope has developed a next-generation SWG, capable of handling modern day concerns, like cloud-based-vulnerabilities, to ensure organisations can utilise cloud storage solutions.
This allows for remote working to operate in unison with preexisting, on-premise infrastructure. With a wide range of new use cases available from this next-generation solution, this blog aims to highlight 5 of the most common, within organisations.
1. Web Filtering
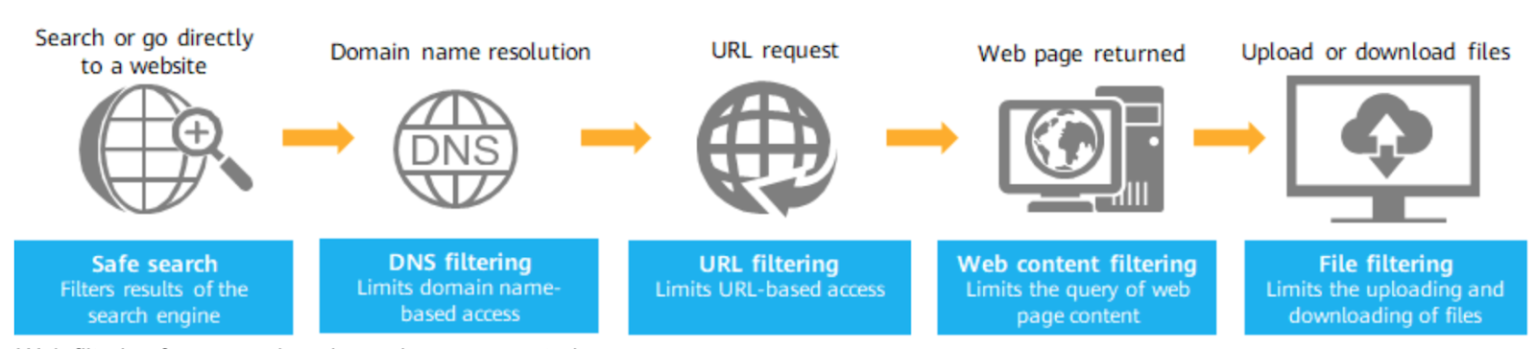
SWGs can be utilised by organisations to control and filter web content accessed by users. Blocking or allowing specific websites or categories is determined by assessing set policies and identifying breaches of these, this assists in the enforcement of acceptable policy use, increasing overall productivity and mitigates the risks associated with accessing inappropriate or malicious content.
Netskope’s next-generation SWG utilises machine learning techniques, in addition to classification databases, to further build on traditional website categorisation. This allows for real-time updating of website classifications by analysing the content of a URL being accessed and either confirming its classification or updating it, if found to be incorrect. Additionally, Netskope’s SWG dynamically classifies websites that have not been determined by any classification vendor, providing further coverage.
2. Malware & Threat Protection
Malware can have a huge impact on organisation functionality. From interrupting and disabling services, to a complete breakdown of an entire Enterprise’s Network Infrastructure, successfully intercepting and preventing the deployment of malware is critical.
SWGs assist in the prevention of Malware attacks, providing protection against web-based threats (malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, etc.). A variety of security mechanisms are incorporated, these include: real-time scanning, threat intelligence and URL reputation checks to block access to malicious websites and prevent users from inadvertently downloading or executing malicious content.
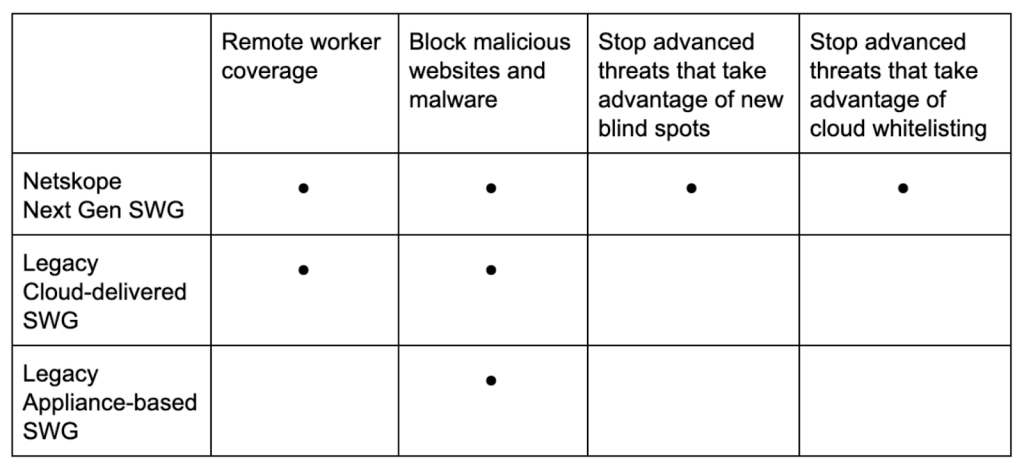
However, with the introduction and utilisation of remote-workers, traditional legacy SWGs are not equipped to prevent cloud-based threats as they were designed to be deployed on-premise. Netskope’s next-generation SWG tackles this challenge through a location-independent design, allowing coverage of users regardless of where they work from.
Cloud-enabled risks and vulnerabilities are mitigated by Netskope’s next-generation SWG as it has the capabilities to decode the contextual data of cloud-activities, allowing for the identification of activities that are deemed risky. Granular policy usage allows for the control of singular apps and app instances to effectively prevent unauthorised activities whilst allowing normal business activity to commence. Legacy appliance-based SWGs ultimately fail to secure cloud-based activity and applications and leave a wide-attack window open when compared to next-generation SWGs.
3. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
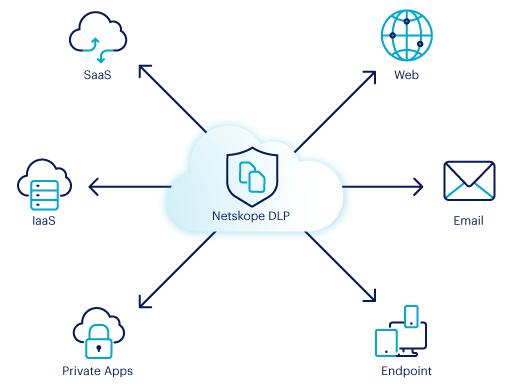
Confidential material is at risk of being exposed or shared through web-traffic, with the average data breach costing $4.24 million to organisations in 2021. SWGs inspect the data of outbound web-traffic, detecting patterns or keywords that could indicate that sensitive material is being trafficked through the web where policies would then be enforced, preventing the transmission. This process helps to mitigate the risk of data-breaches.
Legacy SWGs can produce large amounts of false positives if web traffic is simply looked up for DLP violations, leading to alert fatigue. To combat this, next-generation SWGs use smart inspection, allowing for the collection of data that identifies the context about the target user. With significant increase in the implementation of cloud storage solutions within organisations, it is vital to ensure that cloud activity is also accounted for when adopting a SWG. Netskope’s next-generation SWG utilises a single one-pass DLP inspection, crossing both cloud and web to have complete coverage of all enterprise resources.
4. SSL/TLS Inspection & Assessing Risk
SSL and TLS are utilised to create a secure link when communicating between two networked computers. By offering a 256-bit encryption, it is highly-unlikely that traditional decryption methods can be utilised to expose traffic. SWGs, however, utilise “SSL/TLS inspections” to decrypt and then identify possible threats and policy violations before re-encrypting the traffic. This allows organisations to identify and block activities deemed malicious that would otherwise be hidden with encrypted connections. This provides greater security and coverage of advanced threats.
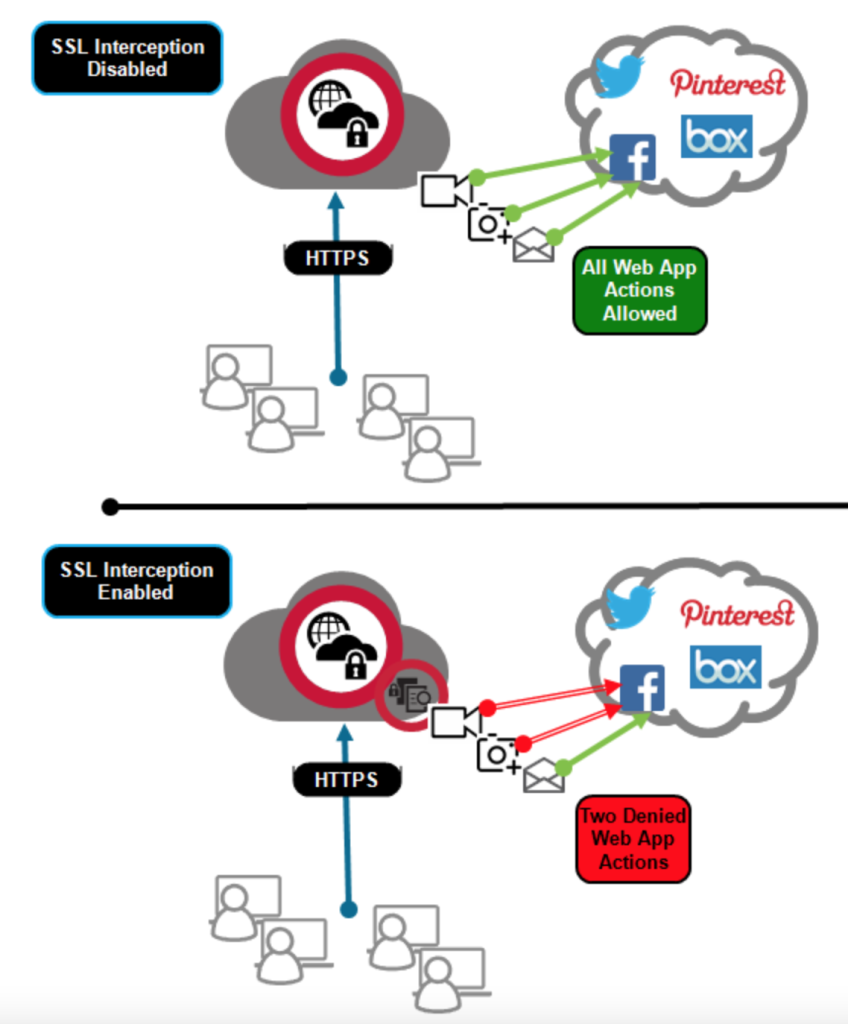
To further eliminate blind-spots, Netskope’s next-generation SWG also decodes API and JSON communications during cloud app communications. This complements the SSL/TLS inspection by providing additional details about the user, their device, their activity, their location and details about the cloud-app and its usage along with the sensitive nature of the content.
Supporting this, Netskope utilises its CCI (Cloud Confidence Index) risk rating to help assure vendors when attempting to identify the security capabilities of a specific Cloud-Application. Before the appropriate policies have been established when using Netskope’s next-generation SWG, data is still tracked wherever it may be during a transmission. Additionally, an alert will be generated whenever data is sent between cloud-applications and whenever data is sent from a corporate user to a personal instance.
5. Direct to Internet Protection
To effectively cover cloud-enabled and advanced web threats, incorporating a cloud-native next-generation SWG can provide effective solutions to ensure high levels of security are met at both cloud and on-premise assets. When securing employees working remotely, Netskope applies a lightweight steering client to send web and cloud traffic towards the Netskope Security Cloud. This is an overall increase to the security of data-in-transmit by providing visibility, control and protection wherever the user goes.
Additionally, when deciding which steering method to use, Dynamic steering can determine where a user is sending data from, whether that is within the organisation’s network or sent remotely. Netskope Security Cloud runs from one of the world largest, most reliable and fastest security networks to ensure performance is never affected, providing secure and reliable access to both the cloud and the web for users when connecting directly to the internet, regardless of location.
Conclusion
Netskope’s next-generation Secure Web Gateway has a more versatile set of use-cases when compared to legacy SWGs, enabling organisations to effectively secure cloud operations and ensure that even users working remotely have the highest security when accessing the cloud and web.
More Resources like this one:
Netskope Technical Introductory Podcast—
Industry-leading CASB Platform Explained
Introduction to Netskope Borderless SD-WAN — Conceptual Overview | Ft. Netskope NewEdge Network
Get in Touch
Contact Jake or the rest of our pre-sales team through our contact form.







